
 According to the Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE), Brazil's production of sugarcane will increase from 514,1 million tonnes this season, to a record 561,8 million tonnes in the 2008/09 cyclus - an increase of 9.3%. New numbers are also out for the 2007 harvest in Brazil's main sugarcane growing region, the Central-South: a record 425 million tonnes compared to 372,7 million tonnes in 2006, or a 14% increase. The estimate was provided by Unica – the União da Indústria de Cana-de-Açúcar.
Jornal Cana - December 16, 2007. According to the Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE), Brazil's production of sugarcane will increase from 514,1 million tonnes this season, to a record 561,8 million tonnes in the 2008/09 cyclus - an increase of 9.3%. New numbers are also out for the 2007 harvest in Brazil's main sugarcane growing region, the Central-South: a record 425 million tonnes compared to 372,7 million tonnes in 2006, or a 14% increase. The estimate was provided by Unica – the União da Indústria de Cana-de-Açúcar.
Jornal Cana - December 16, 2007.
 The University of East Anglia and the UK Met Office's Hadley Centre have today released preliminary global temperature figures for 2007, which show the top 11 warmest years all occurring in the last 13 years. The provisional global figure for 2007 using data from January to November, currently places the year as the seventh warmest on records dating back to 1850. The announcement comes as the Secretary-General of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), Michel Jarraud, speaks at the Conference of the Parties (COP) in Bali.
Eurekalert - December 13, 2007. The University of East Anglia and the UK Met Office's Hadley Centre have today released preliminary global temperature figures for 2007, which show the top 11 warmest years all occurring in the last 13 years. The provisional global figure for 2007 using data from January to November, currently places the year as the seventh warmest on records dating back to 1850. The announcement comes as the Secretary-General of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), Michel Jarraud, speaks at the Conference of the Parties (COP) in Bali.
Eurekalert - December 13, 2007.
 The Royal Society of Chemistry has announced it will launch a new journal in summer 2008, Energy & Environmental Science, which will distinctly address both energy and environmental issues. In recognition of the importance of research in this subject, and the need for knowledge transfer between scientists throughout the world, from launch the RSC will make issues of Energy & Environmental Science available free of charge to readers via its website, for the first 18 months of publication. This journal will highlight the important role that the chemical sciences have in solving the energy problems we are facing today. It will link all aspects of energy and the environment by publishing research relating to energy conversion and storage, alternative fuel technologies, and environmental science.
AlphaGalileo - December 10, 2007. The Royal Society of Chemistry has announced it will launch a new journal in summer 2008, Energy & Environmental Science, which will distinctly address both energy and environmental issues. In recognition of the importance of research in this subject, and the need for knowledge transfer between scientists throughout the world, from launch the RSC will make issues of Energy & Environmental Science available free of charge to readers via its website, for the first 18 months of publication. This journal will highlight the important role that the chemical sciences have in solving the energy problems we are facing today. It will link all aspects of energy and the environment by publishing research relating to energy conversion and storage, alternative fuel technologies, and environmental science.
AlphaGalileo - December 10, 2007.
 Dutch researcher Bas Bougie has developed a laser system to investigate soot development in diesel engines. Small soot particles are not retained by a soot filter but are, however, more harmful than larger soot particles. Therefore, soot development needs to be tackled at the source. Laser Induced Incandescence is a technique that reveals exactly where soot is generated and can be used by project partners to develop cleaner diesel engines. Terry Meyer, an Iowa State University assistant professor of mechanical engineering, is using similar laser technology to develop advanced sensors capable of screening the combustion behavior and soot characteristics specifically of biofuels.
Eurekalert - December 7, 2007. Dutch researcher Bas Bougie has developed a laser system to investigate soot development in diesel engines. Small soot particles are not retained by a soot filter but are, however, more harmful than larger soot particles. Therefore, soot development needs to be tackled at the source. Laser Induced Incandescence is a technique that reveals exactly where soot is generated and can be used by project partners to develop cleaner diesel engines. Terry Meyer, an Iowa State University assistant professor of mechanical engineering, is using similar laser technology to develop advanced sensors capable of screening the combustion behavior and soot characteristics specifically of biofuels.
Eurekalert - December 7, 2007.
 Lithuania's first dedicated biofuel terminal has started operating in Klaipeda port. At the end of November 2007, the stevedoring company Vakaru krova (VK) started activities to manage transshipments. The infrastructure of the biodiesel complex allows for storage of up to 4000 cubic meters of products. During the first year, the terminal plans to transship about 70.000 tonnes of methyl ether, after that the capacities of the terminal would be increased. Investments to the project totaled €2.3 million.
Agrimarket - December 5, 2007. Lithuania's first dedicated biofuel terminal has started operating in Klaipeda port. At the end of November 2007, the stevedoring company Vakaru krova (VK) started activities to manage transshipments. The infrastructure of the biodiesel complex allows for storage of up to 4000 cubic meters of products. During the first year, the terminal plans to transship about 70.000 tonnes of methyl ether, after that the capacities of the terminal would be increased. Investments to the project totaled €2.3 million.
Agrimarket - December 5, 2007.
 New Holland supports the use of B100 biodiesel in all equipment with New Holland-manufactured diesel engines, including electronic injection engines with common rail technology. Overall, nearly 80 percent of the tractor and equipment manufacturer's New Holland-branded products with diesel engines are now available to operate on B100 biodiesel. Tractor and equipment maker John Deere meanwhile clarified its position for customers that want to use biodiesel blends up to B20.
Grainnet - December 5, 2007. New Holland supports the use of B100 biodiesel in all equipment with New Holland-manufactured diesel engines, including electronic injection engines with common rail technology. Overall, nearly 80 percent of the tractor and equipment manufacturer's New Holland-branded products with diesel engines are now available to operate on B100 biodiesel. Tractor and equipment maker John Deere meanwhile clarified its position for customers that want to use biodiesel blends up to B20.
Grainnet - December 5, 2007.
 According to Wetlands International, an NGO, the Kyoto Protocol as it currently stands does not take into account possible emissions from palm oil grown on a particular type of land found in Indonesia and Malaysia, namely peatlands.
Mongabay - December 5, 2007. According to Wetlands International, an NGO, the Kyoto Protocol as it currently stands does not take into account possible emissions from palm oil grown on a particular type of land found in Indonesia and Malaysia, namely peatlands.
Mongabay - December 5, 2007.
 Malaysia's oil & gas giant Petronas considers entering the biofuels sector. Zamri Jusoh, senior manager of Petronas' petroleum development management unit told reporters "of course our focus is on oil and gas, but I think as we move into the future we cannot ignore the importance of biofuels."
AFP - December 5, 2007. Malaysia's oil & gas giant Petronas considers entering the biofuels sector. Zamri Jusoh, senior manager of Petronas' petroleum development management unit told reporters "of course our focus is on oil and gas, but I think as we move into the future we cannot ignore the importance of biofuels."
AFP - December 5, 2007.
 In just four months, the use of biodiesel in the transport sector has substantially improved air quality in Metro Manila, data from the Philippines Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) showed. A blend of one percent coco-biodiesel is mandated by the Biofuels Act of 2007 which took effect last May. By 2009, it would be increased to two percent.
Philippine Star - December 4, 2007. In just four months, the use of biodiesel in the transport sector has substantially improved air quality in Metro Manila, data from the Philippines Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) showed. A blend of one percent coco-biodiesel is mandated by the Biofuels Act of 2007 which took effect last May. By 2009, it would be increased to two percent.
Philippine Star - December 4, 2007.
 Kazakhstan will next year adopt laws to regulate its fledgling biofuel industry and plans to construct at least two more plants in the next 18 months to produce environmentally friendly fuel from crops, industry officials said. According to Akylbek Kurishbayev, vice-minister for agriculture, he Central Asian country has the potential to produce 300,000 tons a year of biodiesel and export half. Kazakhstan could also produce up to 1 billion liters of bioethanol, he said. "The potential is huge. If we use this potential wisely, we can become one of the world's top five producers of biofuels," Beisen Donenov, executive director of the Kazakhstan Biofuels Association, said on the sidelines of a grains forum.
Reuters - November 30, 2007. Kazakhstan will next year adopt laws to regulate its fledgling biofuel industry and plans to construct at least two more plants in the next 18 months to produce environmentally friendly fuel from crops, industry officials said. According to Akylbek Kurishbayev, vice-minister for agriculture, he Central Asian country has the potential to produce 300,000 tons a year of biodiesel and export half. Kazakhstan could also produce up to 1 billion liters of bioethanol, he said. "The potential is huge. If we use this potential wisely, we can become one of the world's top five producers of biofuels," Beisen Donenov, executive director of the Kazakhstan Biofuels Association, said on the sidelines of a grains forum.
Reuters - November 30, 2007.
 SRI Consulting released a report on chemicals from biomass. The analysis highlights six major contributing sources of green and renewable chemicals: increasing production of biofuels will yield increasing amounts of biofuels by-products; partial decomposition of certain biomass fractions can yield organic chemicals or feedstocks for the manufacture of various chemicals; forestry has been and will continue to be a source of pine chemicals; evolving fermentation technology and new substrates will also produce an increasing number of chemicals.
Chemical Online - November 27, 2007. SRI Consulting released a report on chemicals from biomass. The analysis highlights six major contributing sources of green and renewable chemicals: increasing production of biofuels will yield increasing amounts of biofuels by-products; partial decomposition of certain biomass fractions can yield organic chemicals or feedstocks for the manufacture of various chemicals; forestry has been and will continue to be a source of pine chemicals; evolving fermentation technology and new substrates will also produce an increasing number of chemicals.
Chemical Online - November 27, 2007.
 German industrial conglomerate MAN AG plans to expand into renewable energies such as biofuels and solar power. Chief Executive Hakan Samuelsson said services unit Ferrostaal would lead the expansion.
Reuters - November 24, 2007. German industrial conglomerate MAN AG plans to expand into renewable energies such as biofuels and solar power. Chief Executive Hakan Samuelsson said services unit Ferrostaal would lead the expansion.
Reuters - November 24, 2007.
 Analysts think Vancouver-based Ballard Power Systems, which pumped hundreds of millions and decades of research into developing hydrogen fuel cells for cars, is going to sell its automotive division. Experts describe the development as "the death of the hydrogen highway". The problems with H2 fuel cell cars are manifold: hydrogen is a mere energy carrier and its production requires a primary energy input; production is expensive, as would be storage and distribution; finally, scaling fuel cells and storage tanks down to fit in cars remains a huge challenge. Meanwhile, critics have said that the primary energy for hydrogen can better be used for electricity and electric vehicles. On a well-to-wheel basis, the cleanest and most efficient way to produce hydrogen is via biomass, so the news is a set-back for the biohydrogen community. But then again, biomass can be used more efficiently as electricity for battery cars.
Canada.com - November 21, 2007. Analysts think Vancouver-based Ballard Power Systems, which pumped hundreds of millions and decades of research into developing hydrogen fuel cells for cars, is going to sell its automotive division. Experts describe the development as "the death of the hydrogen highway". The problems with H2 fuel cell cars are manifold: hydrogen is a mere energy carrier and its production requires a primary energy input; production is expensive, as would be storage and distribution; finally, scaling fuel cells and storage tanks down to fit in cars remains a huge challenge. Meanwhile, critics have said that the primary energy for hydrogen can better be used for electricity and electric vehicles. On a well-to-wheel basis, the cleanest and most efficient way to produce hydrogen is via biomass, so the news is a set-back for the biohydrogen community. But then again, biomass can be used more efficiently as electricity for battery cars.
Canada.com - November 21, 2007.
 South Korea plans to invest 20 billion won (€14.8/$21.8 million) by 2010 on securing technologies to develop synthetic fuels from biomass, coal and natural gas, as well as biobutanol. 29 private companies, research institutes and universities will join this first stage of the "next-generation clean energy development project" led by South Korea's Ministry of Commerce, Industry and Energy.
Korea Times - November 19, 2007. South Korea plans to invest 20 billion won (€14.8/$21.8 million) by 2010 on securing technologies to develop synthetic fuels from biomass, coal and natural gas, as well as biobutanol. 29 private companies, research institutes and universities will join this first stage of the "next-generation clean energy development project" led by South Korea's Ministry of Commerce, Industry and Energy.
Korea Times - November 19, 2007.
 OPEC leaders began a summit today with Venezuelan President Hugo Chavez issuing a chilling warning that crude prices could double to US$200 from their already-record level if the United States attacked Iran or Venezuela. He urged assembled leaders from the OPEC, meeting for only the third time in the cartel's 47-year history, to club together for geopolitical reasons. But the cartel is split between an 'anti-US' block including Venezuela, Iran, and soon to return ex-member Ecuador, and a 'neutral' group comprising most Gulf States.
France24 - November 17, 2007. OPEC leaders began a summit today with Venezuelan President Hugo Chavez issuing a chilling warning that crude prices could double to US$200 from their already-record level if the United States attacked Iran or Venezuela. He urged assembled leaders from the OPEC, meeting for only the third time in the cartel's 47-year history, to club together for geopolitical reasons. But the cartel is split between an 'anti-US' block including Venezuela, Iran, and soon to return ex-member Ecuador, and a 'neutral' group comprising most Gulf States.
France24 - November 17, 2007.
 The article "Biofuels: What a Biopact between North and South could achieve" published in the scientific journal Energy Policy (Volume 35, Issue 7, 1 July 2007, Pages 3550-3570) ranks number 1 in the 'Top 25 hottest articles'. The article was written by professor John A. Mathews, Macquarie University (Sydney, Autralia), and presents a case for a win-win bioenergy relationship between the industrialised and the developing world. Mathews holds the Chair of Strategic Management at the university, and is a leading expert in the analysis of the evolution and emergence of disruptive technologies and their global strategic management.
ScienceDirect - November 16, 2007. The article "Biofuels: What a Biopact between North and South could achieve" published in the scientific journal Energy Policy (Volume 35, Issue 7, 1 July 2007, Pages 3550-3570) ranks number 1 in the 'Top 25 hottest articles'. The article was written by professor John A. Mathews, Macquarie University (Sydney, Autralia), and presents a case for a win-win bioenergy relationship between the industrialised and the developing world. Mathews holds the Chair of Strategic Management at the university, and is a leading expert in the analysis of the evolution and emergence of disruptive technologies and their global strategic management.
ScienceDirect - November 16, 2007.

|
|
|
|
|
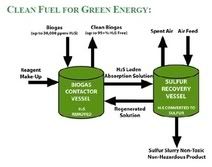 Ontario based Eco-Tec announces that it has been awarded the contract for a biogas purification system by the Régie de gestion des matières résiduelles de la Mauricie (RGMRM) of Quebec. The integrated process includes the capture, purification and use of biogas as an renewable energy source for greenhouses. Growing products in greenhouses is highly energy intensive, making a switch to the use of locally available biomass waste economical.
Ontario based Eco-Tec announces that it has been awarded the contract for a biogas purification system by the Régie de gestion des matières résiduelles de la Mauricie (RGMRM) of Quebec. The integrated process includes the capture, purification and use of biogas as an renewable energy source for greenhouses. Growing products in greenhouses is highly energy intensive, making a switch to the use of locally available biomass waste economical. energy :: sustainability :: biomass :: bioenergy :: biofuels :: landfill :: biogas :: purification :: cogeneration ::
energy :: sustainability :: biomass :: bioenergy :: biofuels :: landfill :: biogas :: purification :: cogeneration ::  --------------
--------------
 According to the Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE), Brazil's production of sugarcane will increase from 514,1 million tonnes this season, to a record 561,8 million tonnes in the 2008/09 cyclus - an increase of 9.3%. New numbers are also out for the 2007 harvest in Brazil's main sugarcane growing region, the Central-South: a record 425 million tonnes compared to 372,7 million tonnes in 2006, or a 14% increase. The estimate was provided by Unica – the União da Indústria de Cana-de-Açúcar.
According to the Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE), Brazil's production of sugarcane will increase from 514,1 million tonnes this season, to a record 561,8 million tonnes in the 2008/09 cyclus - an increase of 9.3%. New numbers are also out for the 2007 harvest in Brazil's main sugarcane growing region, the Central-South: a record 425 million tonnes compared to 372,7 million tonnes in 2006, or a 14% increase. The estimate was provided by Unica – the União da Indústria de Cana-de-Açúcar.








2 Comments:
You are still going to have the CO2, making the quality far from Natural Gas. It's ~ 600 BTU/cu.ft vs. 1000 BTU/cu.ft.
^
Post a Comment
Links to this post:
Create a Link
<< Home