U.S. oil production down 5%, reserves declined 4% in 2006; natural gas reserves and production up
 According to an advance report [*.pdf] by the Energy Information Administration (EIA) of the U.S. Department of Energy, crude oil production declined 5 percent in 2006 whereas proved reserves were down by 4 percent in 2006. The U.S. is the third largest oil producer after Saudi Arabia and Russia. U.S. natural gas proved reserves on the contrary increased 3 percent in 2006, rising to over 211 trillion cubic feet, the highest level since 1976. Additions to reserves replaced 136 percent of the dry natural gas produced in 2006. This was the eighth year in a row that U.S. natural gas proved reserves have increased.
According to an advance report [*.pdf] by the Energy Information Administration (EIA) of the U.S. Department of Energy, crude oil production declined 5 percent in 2006 whereas proved reserves were down by 4 percent in 2006. The U.S. is the third largest oil producer after Saudi Arabia and Russia. U.S. natural gas proved reserves on the contrary increased 3 percent in 2006, rising to over 211 trillion cubic feet, the highest level since 1976. Additions to reserves replaced 136 percent of the dry natural gas produced in 2006. This was the eighth year in a row that U.S. natural gas proved reserves have increased.Crude oil
According to the report, the Gulf of Mexico Federal Offshore and Alaska, two of the largest U.S. oil-producing areas, reported 10 and 7 percent declines in crude oil proved reserves. This was due to downward revisions and fewer new discoveries. Utah reported the largest increase in crude oil reserves, adding 78 million barrels (a 30 percent increase from 2005), followed by Colorado and New Mexico.
Reserves additions of crude oil did not keep pace with production - operators replaced only 52 percent of 2006 crude oil production with reserves additions. U.S. crude oil production declined 5 percent in 2006 due mostly to lower Alaskan production. Part of the decline resulted from an August 2006 shut-in of producing wells in half of Prudhoe Bay Field for inspection and repair of corrosion in the gathering system.
For the second year in a row Montana had the largest annual oil production increase of any State (6 million barrels; a 20 percent increase) owing to continued development of the Bakken Formation in the Elm Coulee Field. This relatively new and important oil field is difficult to produce and requires cutting-edge technology for economic production.
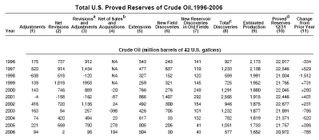
Total discoveries of crude oil were 577 million barrels in 2006, 49 percent less than the prior 10-year average and 45 percent less than 2005's discoveries of 1,051 million barrels (table, click to enlarge).
The majority of crude oil total discoveries in 2006 came from extensions to fields in Texas, Alaska, the Gulf of Mexico Federal Offshore, Montana, California, New Mexico, and Louisiana.
Operators discovered 504 million barrels in extensions in 2006, 37 percent less than in 2005 and 10 percent less than the prior 10-year average (558 million barrels).
New field discoveries accounted for 30 million barrels of crude oil reserves additions. Seventy percent of these discoveries (21 of 30 million barrels) were in the Gulf of Mexico Federal Offshore. This was 85 percent less than the new field discoveries of 2005 and only 7 percent of the prior 10-year average (428 million barrels):
 energy :: sustainability :: oil fields :: oil discoveries :: reserves :: crude oil :: natural gas :: Peak Oil :: United States ::
energy :: sustainability :: oil fields :: oil discoveries :: reserves :: crude oil :: natural gas :: Peak Oil :: United States :: New reservoir discoveries in old fields were 43 million barrels, 5 percent more than 2005 and 71 percent less than the prior 10-year average (149 million barrels).
Reserves additions are the sum of total discoveries, revisions, adjustments, sales, and acquisitions. In 2006, reserves additions were 867 million barrels, 59 percent less than the volume of reserves additions in 2005 and 54 percent less than the prior 10-year average (1,876 million barrels).
Crude oil net revisions and adjustments were 96 million barrels, 88 percent less than the net revisions and adjustments of 2005 and only 13 percent of the prior 10-year average (759 million barrels). The net of sales and acquisitions of crude oil proved reserves was 194 million barrels.
Other 2006 crude oil events of note:
• The annual average domestic first purchase price for crude oil increased 19 percent from $50.28 per barrel in 2005 to $59.69 per barrel.
• Oil well completions (exploratory and development) were up 28 percent from 2005.
Natural gas
Texas led the nation in natural gas reserves additions in 2006 with a 9 percent increase in dry gas proved reserves due to rapid development of Barnett Shale reservoirs in the Newark East Field. Advances in horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing technology and relatively high natural gas prices supported this development.
Alaska and Utah were second and third for dry natural gas proved reserves additions in 2006. Total U.S. natural gas production increased in 2006 due to production increases in Texas (Barnett Shale), Louisiana, and the Rocky Mountain states (Colorado, Wyoming, Utah, and Montana). Gulf of Mexico natural gas production declined the most with a 6 percent drop.
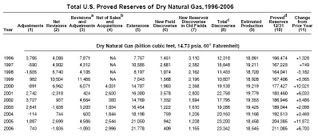
Total discoveries of dry natural gas reserves attributed to the drilling of exploratory wells, which include field extensions, new field discoveries, and new reservoir discoveries in old fields, were 23,342 billion cubic feet in 2006. This was 35 percent more than the prior 10-year average (17,255 billion cubic feet) and 1 percent more than in 2005 (table, click to enlarge).
The majority of natural gas total discoveries in 2006 were from extensions to existing gas fields. Field extensions were 21,778 billion cubic feet, 3 percent more than in 2005 and 61 percent more than the prior 10-year average (13,522 billion cubic feet).
New field discoveries were 409 billion cubic feet, 57 percent less than the volume discovered in 2005 and 75 percent less than the prior 10-year average (1,659 billion cubic feet).
New reservoir discoveries in old fields were 1,155 billion cubic feet, 4 percent less than 2005 and 44 percent less than the prior 10-year average (2,074 billion cubic feet).
Natural gas net revisions and adjustments were a net loss of 1,093 billion cubic feet in 2006. The prior occurrence of negative net revisions was in 1988. The net of sales and acquisitions of dry natural gas proved reserves was 2,996 billion cubic feet.
Coalbed natural gas reserves decreased 1 percent in 2006 and accounted for 9 percent of U.S. dry natural gas reserves. Coalbed natural gas production increased 2 percent in 2006 and accounted for 9 percent of U.S. dry natural gas production.
Other 2006 natural gas events of note:
• Natural gas prices at the wellhead declined 12 percent in 2006 to an average of $6.42 per thousand cubic feet, as compared to $7.33 per thousand cubic feet in 2005.
• Gas well completions (exploratory and development) were up 17 percent from 2005.
References:
Energy Information Administration: U.S. Natural Gas Proved Reserves Reach 30 Year High in 2006 Alaska and Gulf of Mexico Oil Reserves Revised Downward - November 5, 2007.
Energy Information Administration: Advance Summary: U.S. Crude Oil, Natural Gas, and Natural Gas Liquids Reserves 2006 Annual Report [*.pdf] - October, 2007
 --------------
--------------
 German industrial conglomerate MAN AG plans to expand into renewable energies such as biofuels and solar power. Chief Executive Hakan Samuelsson said services unit Ferrostaal would lead the expansion.
German industrial conglomerate MAN AG plans to expand into renewable energies such as biofuels and solar power. Chief Executive Hakan Samuelsson said services unit Ferrostaal would lead the expansion.








0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Links to this post:
Create a Link
<< Home