EU greenhouse gas emissions decreased 0.8% in 2005
 Emissions of climate-changing greenhouse gases (GHG) decreased between 2004 and 2005, according to the annual GHG inventory report of the European Community prepared by the European Environment Agency (EEA), in Copenhagen. The report, 'Annual European Community Greenhouse gas inventory 1990-2005 and inventory report 2007', was submitted to the secretariat of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) as the European Community's official submission. The EEA released the main, preliminary, messages of the report in May 2007 because of public and political interest in the issue of climate change. The final version of this report was submitted to the UNFCCC on 27 May 2007.
Emissions of climate-changing greenhouse gases (GHG) decreased between 2004 and 2005, according to the annual GHG inventory report of the European Community prepared by the European Environment Agency (EEA), in Copenhagen. The report, 'Annual European Community Greenhouse gas inventory 1990-2005 and inventory report 2007', was submitted to the secretariat of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) as the European Community's official submission. The EEA released the main, preliminary, messages of the report in May 2007 because of public and political interest in the issue of climate change. The final version of this report was submitted to the UNFCCC on 27 May 2007.Interactive GHG dataviewers allow the user to compile and compare emissions data per sector and per country over a given time-frame.
The key points of the final report are:
- EU-15: Emissions of GHGs decreased by 0.8% (35.2 million tonnes CO2 equivalents) between 2004 and 2005 - mainly due to decreasing CO2 emissions of 0.7 % (26 million tonnes).
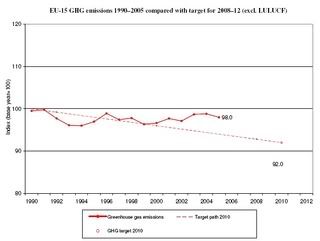
- EU-15: Emissions of GHGs decreased by 2.0% in 2005 compared to the base year under the Kyoto Protocol (graph, click to enlarge).
- EU-15: Emissions of GHGs decreased by 1.5% between 1990 and 2005
- EU-27: Emissions of GHGs decreased by 0.7% (37.9 million tonnes CO2 equivalents) between 2004 and 2005
- EU-27: Emissions of GHGs decreased by 7.9% compared to 1990 levels
Emissions per sector
In absolute terms, the main sectors contributing to emissions reductions between 2004 and 2005 in the EU-15 were public electricity and heat production, households and services, and road transport.
- CO2 emissions from public electricity and heat production decreased by 0.9% (-9.6 million tonnes) mainly due to a reduction in the reliance on coal.
- CO2 emissions from households and services decreased by 1.7 % (7.0 million tonnes). Important decreases in emissions from household and services were reported by Germany, the United Kingdom and the Netherlands. One general reason for the decrease is the warmer weather conditions (milder winter) compared to the previous year.
- CO2 emissions from road transport decreased by 0.8% (6 million tonnes). This is mainly attributed to Germany, and is due to increased amounts of diesel oil driven cars, the effects of the eco-tax and fuel buying from outside Germany (fuel tourism).
In absolute terms, Spain increased greenhouse gas emissions the most between 2004 and 2005.
In Spain, the increase in greenhouse gas emissions by 3.6% or 15.4 million tonnes CO2 equivalents came mainly from public electricity and heat production. This is due to a rise in electricity generation from fossil thermal power stations (17 %) and a decrease in electricity generation from hydropower plants (-33 %).
Other EU-15 countries which saw emissions increase between 2004 and 2005 are: Austria, Greece, Ireland, Italy and Portugal:
 biofuels :: energy :: sustainability :: climate change :: greenhouse gas emissions :: CO2 :: Kyoto Protocol :: EU ETS :: European Union ::
biofuels :: energy :: sustainability :: climate change :: greenhouse gas emissions :: CO2 :: Kyoto Protocol :: EU ETS :: European Union :: Role of the EU Emission Trading Scheme
In 2005 the EU Emission Trading Scheme (EU ETS) covered approximately 47% of the total CO2 emissions and around 39% of total greenhouse gas emissions in EU-15. The EU ETS covered 49% of the total CO2 emission and 41% of total greenhouse gas emissions in EU-25. In general, EU ETS information has been used by EU Member States as one input for calculating total CO2 emissions for the Energy and Industrial Processes sectors in this report. However, an explicit quantification of the contribution of the EU ETS to total CO2 emissions at sectoral and sub-sectoral level is not yet available for EU-15 or EU-25.
Significance for Kyoto Protocol obligations
The EU-15 has a common target under the Kyoto Protocol to reduce total greenhouse gas emissions by 8 %, compared to the base year. The EU-27 does not have a common Kyoto target. Official reporting of emissions for compliance purposes under the Kyoto Protocol does not begin until 2010 – when emissions will be reported for the year 2008. In the meantime, this report is the most relevant and accurate source of information on greenhouse gas emissions for the EU. It can be used for tracking the EU's performance when it comes to reducing domestic greenhouse emissions (i.e. emissions within its territory) towards meeting the Kyoto targets. Parties to the Kyoto Protocol are allowed to use carbon sinks as well as the so called 'flexible mechanisms' to further reduce greenhouse gas emissions outside their national territories - as a supplement to domestic reductions. Hence, domestic action is the primary method of achieving the Kyoto targets. This inventory report suggests that domestic emissions of GHGs decreased by approximately 2.0 % compared to the base year under the Kyoto Protocol.
More information:
European Environment Agency: Annual European Community greenhouse gas inventory 1990-2005 and inventory report 2007, Technical report No 7/2007, June 17, 2007.
European Environment Agency GHG data viewers.
 --------------
--------------
 Mongabay, a leading resource for news and perspectives on environmental and conservation issues related to the tropics, has launched Tropical Conservation Science - a new, open access academic e-journal. It will cover a wide variety of scientific and social studies on tropical ecosystems, their biodiversity and the threats posed to them.
Mongabay, a leading resource for news and perspectives on environmental and conservation issues related to the tropics, has launched Tropical Conservation Science - a new, open access academic e-journal. It will cover a wide variety of scientific and social studies on tropical ecosystems, their biodiversity and the threats posed to them.









1 Comments:
EEA's GHG data viewer has been updated in June2008,
See the new EEA's GHG data viewers @:
http://dataservice.eea.europa.eu/PivotApp/pivot.aspx?pivotid=455
Post a Comment
Links to this post:
Create a Link
<< Home