ESA satellite images aid implementation of agricultural reforms
Brazilian ethanol production is highly efficient and sustainable, in part thanks to the utilisation of earth observation (EO) techniques that allow sugarcane farmers and researchers to plan each plot carefully, to monitor productivity, pests and diseases and a host of other agronomic parameters. From the European Space Agency now comes another interesting example of how satellite images can assist in thorough monitoring and planning of land use. In this case, EO is used to the check the application of so-called cross compliance measures – a set of environmental and animal welfare standards that farmers have to respect to receive full funding from the European Union – included in the 2003 reforms of the Common Agricultural Policy.
The ever increasing number of highly finetuned EO-based land use monitoring techniques must make it possible in the future to organise a form of planetary biomass management, that allows us to analyse the optimal distribution of where what types of crop can be grown best, and what kinds of environmental standards should be applied in order to ensure long term sustainability - on a truly planetary scale.
ESA's example demonstrates how very high resolution (VHR) satellite images can monitor whether land is safeguarded in 'Good Agricultural and Environmental Condition' (GAEC) - this information consequently ensures EU subsidies are distributed in a fair and timely manner and helps farmers complete subsidy applications more accurately. One of those subsidies involves energy crops, that must be grown on set-aside land.
High resolution satellites as well as aerial photography have been used for some time to monitor areas where subsidies are provided. VHR EO satellites, however, offer more detail compared with HR satellites and are capable of identifying various landscape features and detecting potential erosion, tillage practices and maintenance of pastures:
 bioenergy :: biofuels :: energy :: sustainability :: land use :: earth observation :: satellite :: ESA :: subsidies :: EU ::
bioenergy :: biofuels :: energy :: sustainability :: land use :: earth observation :: satellite :: ESA :: subsidies :: EU ::
Under the GAEC standards implemented in some countries, farmers cannot remove certain landscape features, including hedges, tree rows, water ponds, walls and single trees, without authorisation of national administration in order to preserve habitats for different organisms and species.
By using special classification procedures on VHR satellite images, identification of these landscape features is possible. In combination with digital aerial images, even single trees can be delineated. By comparing older and recent images of these same areas with the processed ‘reference landscape feature’ layer, the removal of these features can be detected.
To protect soils against erosion risks and improve soil structure, the GAEC as applied in some countries, states farmers must establish an ‘environmental cover’ for a buffer width, stipulated by the country itself (e.g. 5 metres), around waterways on all parcels adjacent to waterways to restrict diffuse pollution in waters and soils.
Pastures, permanent crops, woods, hedges and paths are considered ‘environmental cover’, while mainly arable land and crops are not. Because satellite images allow for the interpretation of agricultural parcels, compliancy can be easily detected. Photo interpretation by remote sensing speeds up the process and allows many parcels to be checked in one time.
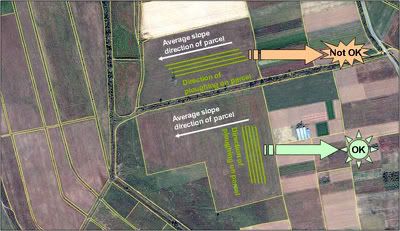
Tillage practices are also important for reducing erosion as they can reduce the runoff of water across the land surface. The GAEC stipulates that farmers have to plough or plant parallel to contour lines to avoid erosion on slopes more than or equal to a certain percentage defined by the country (e.g. slope of 10 percent).
By detecting parcels within this slope range, detecting the slope direction and the ploughing or planting direction, it is possible to calculate the angle between the slope and ploughing direction, taking into account the soil-sensitivity to erosion, and determine whether the farmer is compliant.
In order to receive subsidies for permanent crops, the GAEC requires that farmers properly maintain them. Using VHR images, the distinction between crops that are ‘maintained good’ and crops that are ‘possibly maintained badly’ can be detected, allowing authorities to visit the fields in question to detect whether they are abandoned or neglected.
This project was funded by ESA’s Earth Observation Market Development (EOMD) programme, aimed at fostering the development of EO data within business practices, and carried out by EUROSENSE, a company that specialises in remote sensing.
Movie: By using special classification procedures on very high resolution (VHR) satellite images, identification of landscape features, including hedges, tree rows, water ponds, walls and single trees, is possible. By comparing older and recent images of these same areas with the processed ‘reference landscape feature’ layer, the removal of these features can be detected. Credits: EUROSENSE.
More information:
European Space Agency: "Satellite images aid implementation of agricultural reforms" - April 13, 2007.
EU Commission: "Renewable energy: Commission welcomes Council agreement on extension of energy crop aid scheme to all Member States" - 19 December 2006
European Commission, Agriculture and Rural Development: CAP reform.

ESA's example demonstrates how very high resolution (VHR) satellite images can monitor whether land is safeguarded in 'Good Agricultural and Environmental Condition' (GAEC) - this information consequently ensures EU subsidies are distributed in a fair and timely manner and helps farmers complete subsidy applications more accurately. One of those subsidies involves energy crops, that must be grown on set-aside land.
High resolution satellites as well as aerial photography have been used for some time to monitor areas where subsidies are provided. VHR EO satellites, however, offer more detail compared with HR satellites and are capable of identifying various landscape features and detecting potential erosion, tillage practices and maintenance of pastures:
 bioenergy :: biofuels :: energy :: sustainability :: land use :: earth observation :: satellite :: ESA :: subsidies :: EU ::
bioenergy :: biofuels :: energy :: sustainability :: land use :: earth observation :: satellite :: ESA :: subsidies :: EU :: Under the GAEC standards implemented in some countries, farmers cannot remove certain landscape features, including hedges, tree rows, water ponds, walls and single trees, without authorisation of national administration in order to preserve habitats for different organisms and species.
By using special classification procedures on VHR satellite images, identification of these landscape features is possible. In combination with digital aerial images, even single trees can be delineated. By comparing older and recent images of these same areas with the processed ‘reference landscape feature’ layer, the removal of these features can be detected.
To protect soils against erosion risks and improve soil structure, the GAEC as applied in some countries, states farmers must establish an ‘environmental cover’ for a buffer width, stipulated by the country itself (e.g. 5 metres), around waterways on all parcels adjacent to waterways to restrict diffuse pollution in waters and soils.
Pastures, permanent crops, woods, hedges and paths are considered ‘environmental cover’, while mainly arable land and crops are not. Because satellite images allow for the interpretation of agricultural parcels, compliancy can be easily detected. Photo interpretation by remote sensing speeds up the process and allows many parcels to be checked in one time.
Tillage practices are also important for reducing erosion as they can reduce the runoff of water across the land surface. The GAEC stipulates that farmers have to plough or plant parallel to contour lines to avoid erosion on slopes more than or equal to a certain percentage defined by the country (e.g. slope of 10 percent).
By detecting parcels within this slope range, detecting the slope direction and the ploughing or planting direction, it is possible to calculate the angle between the slope and ploughing direction, taking into account the soil-sensitivity to erosion, and determine whether the farmer is compliant.
In order to receive subsidies for permanent crops, the GAEC requires that farmers properly maintain them. Using VHR images, the distinction between crops that are ‘maintained good’ and crops that are ‘possibly maintained badly’ can be detected, allowing authorities to visit the fields in question to detect whether they are abandoned or neglected.
This project was funded by ESA’s Earth Observation Market Development (EOMD) programme, aimed at fostering the development of EO data within business practices, and carried out by EUROSENSE, a company that specialises in remote sensing.
Movie: By using special classification procedures on very high resolution (VHR) satellite images, identification of landscape features, including hedges, tree rows, water ponds, walls and single trees, is possible. By comparing older and recent images of these same areas with the processed ‘reference landscape feature’ layer, the removal of these features can be detected. Credits: EUROSENSE.
More information:
European Space Agency: "Satellite images aid implementation of agricultural reforms" - April 13, 2007.
EU Commission: "Renewable energy: Commission welcomes Council agreement on extension of energy crop aid scheme to all Member States" - 19 December 2006
European Commission, Agriculture and Rural Development: CAP reform.
 --------------
--------------
 Vietnam has won the prestigious EU-sponsored Energy Globe award for 2006 for a community biogas program, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development announced.
Vietnam has won the prestigious EU-sponsored Energy Globe award for 2006 for a community biogas program, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development announced.








0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Links to this post:
Create a Link
<< Home