


 Saab will introduce its BioPower flex-fuel options to its entire 9-3 range, including Sport Sedan, SportCombi and Convertible bodystyles, at the Geneva auto show.
GreenCarCongress - March 2, 2007. Saab will introduce its BioPower flex-fuel options to its entire 9-3 range, including Sport Sedan, SportCombi and Convertible bodystyles, at the Geneva auto show.
GreenCarCongress - March 2, 2007.
 British oil giant BP plans to invest around US$50 million in Indonesia's biofuel industry, using jatropha oil as feedstock. BP will build biofuel plants with an annual capacity of 350,000 tons for which it will need to set up jatropha curcas plantations covering 100,000 hectares of land, to guarantee supply of feedstock, an official said.
Antara [*cache] - March 2, 2007. British oil giant BP plans to invest around US$50 million in Indonesia's biofuel industry, using jatropha oil as feedstock. BP will build biofuel plants with an annual capacity of 350,000 tons for which it will need to set up jatropha curcas plantations covering 100,000 hectares of land, to guarantee supply of feedstock, an official said.
Antara [*cache] - March 2, 2007.
 The government of Taiwan has decided to increase the acreage dedicated to biofuel crops -- soybean, rape, sunflower, and sweet potato -- from 1,721 hectares in 2006 to 4,550 hectares this year, the Council of Agriculture said.
China Post - March 2, 2007. The government of Taiwan has decided to increase the acreage dedicated to biofuel crops -- soybean, rape, sunflower, and sweet potato -- from 1,721 hectares in 2006 to 4,550 hectares this year, the Council of Agriculture said.
China Post - March 2, 2007.
 Kinder Morgan Energy Partners has announced plans to invest up to €76/US$100 million to expand its terminal facilities to help serve the growing biodiesel market. KMP has entered into long-term agreements with Green Earth Fuels, LLC to build up to 1.3 million barrels of tankage that will handle approximately 8 million barrels of biodiesel production at KMP's terminals on the Houston Ship Channel, the Port of New Orleans and in New York Harbor.
PRNewswire - March 1, 2007. Kinder Morgan Energy Partners has announced plans to invest up to €76/US$100 million to expand its terminal facilities to help serve the growing biodiesel market. KMP has entered into long-term agreements with Green Earth Fuels, LLC to build up to 1.3 million barrels of tankage that will handle approximately 8 million barrels of biodiesel production at KMP's terminals on the Houston Ship Channel, the Port of New Orleans and in New York Harbor.
PRNewswire - March 1, 2007.
 A project to build a 130 million euro ($172 million) plant to produce 200,000 cubic metres of bioethanol annually was announced by three German groups on Tuesday. The plant will consume about 600,000 tonnes of wheat annually and when operational in the first half of 2009 should provide about a third of Germany's estimated bioethanol requirements.
Reuters - Feb. 27, 2007. A project to build a 130 million euro ($172 million) plant to produce 200,000 cubic metres of bioethanol annually was announced by three German groups on Tuesday. The plant will consume about 600,000 tonnes of wheat annually and when operational in the first half of 2009 should provide about a third of Germany's estimated bioethanol requirements.
Reuters - Feb. 27, 2007.
 Taiwan's Ministry of Economic Affairs has announced that government vehicles in Taipei City will begin using E3 fuel, composed of 97% gasoline and 3% ethanol, on a trial basis in 2007.
Automotive World - Feb. 27, 2007. Taiwan's Ministry of Economic Affairs has announced that government vehicles in Taipei City will begin using E3 fuel, composed of 97% gasoline and 3% ethanol, on a trial basis in 2007.
Automotive World - Feb. 27, 2007.
 Spanish company Ferry Group is to invest €42/US$55.2 million in a project for the production of biomass fuel pellets in Bulgaria.
The 3-year project consists of establishing plantations of paulownia trees near the city of Tran. Paulownia is a fast-growing tree used for the commercial production of fuel pellets.
Dnevnik - Feb. 20, 2007. Spanish company Ferry Group is to invest €42/US$55.2 million in a project for the production of biomass fuel pellets in Bulgaria.
The 3-year project consists of establishing plantations of paulownia trees near the city of Tran. Paulownia is a fast-growing tree used for the commercial production of fuel pellets.
Dnevnik - Feb. 20, 2007.
 Hungary's BHD Hõerõmû Zrt. is to build a 35 billion Forint (€138/US$182 million) commercial biomass-fired power plant with a maximum output of 49.9 MW in Szerencs (northeast Hungary).
Portfolio.hu - Feb. 20, 2007. Hungary's BHD Hõerõmû Zrt. is to build a 35 billion Forint (€138/US$182 million) commercial biomass-fired power plant with a maximum output of 49.9 MW in Szerencs (northeast Hungary).
Portfolio.hu - Feb. 20, 2007.
 Tonight at 9pm, BBC Two will be showing a program on geo-engineering techniques to 'save' the planet from global warming. Five of the world's top scientists propose five radical scientific inventions which could stop climate change dead in its tracks. The ideas include: a giant sunshade in space to filter out the sun's rays and help cool us down; forests of artificial trees that would breath in carbon dioxide and stop the green house effect and a fleet futuristic yachts that will shoot salt water into the clouds thickening them and cooling the planet.
BBC News - Feb. 19, 2007. Tonight at 9pm, BBC Two will be showing a program on geo-engineering techniques to 'save' the planet from global warming. Five of the world's top scientists propose five radical scientific inventions which could stop climate change dead in its tracks. The ideas include: a giant sunshade in space to filter out the sun's rays and help cool us down; forests of artificial trees that would breath in carbon dioxide and stop the green house effect and a fleet futuristic yachts that will shoot salt water into the clouds thickening them and cooling the planet.
BBC News - Feb. 19, 2007.
 Archer Daniels Midland, the largest U.S. ethanol producer, is planning to open a biodiesel plant in Indonesia with Wilmar International Ltd. this year and a wholly owned biodiesel plant in Brazil before July, the Wall Street Journal reported on Thursday. The Brazil plant is expected to be the nation's largest, the paper said. Worldwide, the company projects a fourfold rise in biodiesel production over the next five years. ADM was not immediately available to comment.
Reuters - Feb. 16, 2007. Archer Daniels Midland, the largest U.S. ethanol producer, is planning to open a biodiesel plant in Indonesia with Wilmar International Ltd. this year and a wholly owned biodiesel plant in Brazil before July, the Wall Street Journal reported on Thursday. The Brazil plant is expected to be the nation's largest, the paper said. Worldwide, the company projects a fourfold rise in biodiesel production over the next five years. ADM was not immediately available to comment.
Reuters - Feb. 16, 2007.
 Finnish engineering firm Pöyry Oyj has been awarded contracts by San Carlos Bioenergy Inc. to provide services for the first bioethanol plant in the Philippines. The aggregate contract value is EUR 10 million. The plant is to be build in the Province of San Carlos on the north-eastern tip of Negros Island. The plant is expected to deliver 120,000 liters/day of bioethanol and 4 MW of excess power to the grid.
Kauppalehti Online - Feb. 15, 2007. Finnish engineering firm Pöyry Oyj has been awarded contracts by San Carlos Bioenergy Inc. to provide services for the first bioethanol plant in the Philippines. The aggregate contract value is EUR 10 million. The plant is to be build in the Province of San Carlos on the north-eastern tip of Negros Island. The plant is expected to deliver 120,000 liters/day of bioethanol and 4 MW of excess power to the grid.
Kauppalehti Online - Feb. 15, 2007.
 In order to reduce fuel costs, a Mukono-based flower farm which exports to Europe, is building its own biodiesel plant, based on using Jatropha curcas seeds. It estimates the fuel will cut production costs by up to 20%.
New Vision (Kampala, Uganda) - Feb. 12, 2007. In order to reduce fuel costs, a Mukono-based flower farm which exports to Europe, is building its own biodiesel plant, based on using Jatropha curcas seeds. It estimates the fuel will cut production costs by up to 20%.
New Vision (Kampala, Uganda) - Feb. 12, 2007.
 The Tokyo Metropolitan Government has decided to use 10% biodiesel in its fleet of public buses. The world's largest city is served by the Toei Bus System, which is used by some 570,000 people daily.
Digital World Tokyo - Feb. 12, 2007. The Tokyo Metropolitan Government has decided to use 10% biodiesel in its fleet of public buses. The world's largest city is served by the Toei Bus System, which is used by some 570,000 people daily.
Digital World Tokyo - Feb. 12, 2007.
 Fearing lack of electricity supply in South Africa and a price tag on CO2, WSP Group SA is investing in a biomass power plant that will replace coal in the Letaba Citrus juicing plant which is located in Tzaneen.
Mining Weekly - Feb. 8, 2007. Fearing lack of electricity supply in South Africa and a price tag on CO2, WSP Group SA is investing in a biomass power plant that will replace coal in the Letaba Citrus juicing plant which is located in Tzaneen.
Mining Weekly - Feb. 8, 2007.
 In what it calls an important addition to its global R&D capabilities, Archer Daniels Midland (ADM) is to build a new bioenergy research center in Hamburg, Germany.
World Grain - Feb. 5, 2007. In what it calls an important addition to its global R&D capabilities, Archer Daniels Midland (ADM) is to build a new bioenergy research center in Hamburg, Germany.
World Grain - Feb. 5, 2007.
 EthaBlog's Henrique Oliveira interviews leading Brazilian biofuels consultant Marcelo Coelho who offers insights into the (foreign) investment dynamics in the sector, the history of Brazilian ethanol and the relationship between oil price trends and biofuels.
EthaBlog - Feb. 2, 2007. EthaBlog's Henrique Oliveira interviews leading Brazilian biofuels consultant Marcelo Coelho who offers insights into the (foreign) investment dynamics in the sector, the history of Brazilian ethanol and the relationship between oil price trends and biofuels.
EthaBlog - Feb. 2, 2007.
 The government of Taiwan has announced its renewable energy target: 12% of all energy should come from renewables by 2020. The plan is expected to revitalise Taiwan's agricultural sector and to boost its nascent biomass industry.
China Post - Feb. 2, 2007. The government of Taiwan has announced its renewable energy target: 12% of all energy should come from renewables by 2020. The plan is expected to revitalise Taiwan's agricultural sector and to boost its nascent biomass industry.
China Post - Feb. 2, 2007.
 Production at Cantarell, the world's second biggest oil field, declined by 500,000 barrels or 25% last year. This virtual collapse is unfolding much faster than projections from Mexico's state-run oil giant Petroleos Mexicanos.
Wall Street Journal - Jan. 30, 2007. Production at Cantarell, the world's second biggest oil field, declined by 500,000 barrels or 25% last year. This virtual collapse is unfolding much faster than projections from Mexico's state-run oil giant Petroleos Mexicanos.
Wall Street Journal - Jan. 30, 2007.
 Dubai-based and AIM listed Teejori Ltd. has entered into an agreement to invest â¬6 million to acquire a 16.7% interest in Bekon, which developed two proprietary technologies enabling dry-fermentation of biomass. Both technologies allow it to design, establish and operate biogas plants in a highly efficient way. Dry-Fermentation offers significant advantages to the existing widely used wet fermentation process of converting biomass to biogas.
Ame Info - Jan. 22, 2007. Dubai-based and AIM listed Teejori Ltd. has entered into an agreement to invest â¬6 million to acquire a 16.7% interest in Bekon, which developed two proprietary technologies enabling dry-fermentation of biomass. Both technologies allow it to design, establish and operate biogas plants in a highly efficient way. Dry-Fermentation offers significant advantages to the existing widely used wet fermentation process of converting biomass to biogas.
Ame Info - Jan. 22, 2007.
 Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited is to build a biofuel production plant in the tribal belt of Banswara, Rajasthan, India. The petroleum company has acquired 20,000 hectares of low value land in the district, which it plans to commit to growing jatropha and other biofuel crops. The company's chairman said HPCL was also looking for similar wasteland in the state of Chhattisgarh.
Zee News - Jan. 15, 2007. Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited is to build a biofuel production plant in the tribal belt of Banswara, Rajasthan, India. The petroleum company has acquired 20,000 hectares of low value land in the district, which it plans to commit to growing jatropha and other biofuel crops. The company's chairman said HPCL was also looking for similar wasteland in the state of Chhattisgarh.
Zee News - Jan. 15, 2007.
 The Zimbabwean national police begins planting jatropha for a pilot project that must result in a daily production of 1000 liters of biodiesel.
The Herald (Harare), Via AllAfrica - Jan. 12, 2007. The Zimbabwean national police begins planting jatropha for a pilot project that must result in a daily production of 1000 liters of biodiesel.
The Herald (Harare), Via AllAfrica - Jan. 12, 2007.
 In order to meet its Kyoto obligations and to cut dependence on oil, Japan has started importing biofuels from Brazil and elsewhere. And even though the country has limited local bioenergy potential, its Agriculture Ministry will begin a search for natural resources, including farm products and their residues, that can be used to make biofuels in Japan. To this end, studies will be conducted at 900 locations nationwide over a three-year period.
The Japan Times - Jan. 12, 2007. In order to meet its Kyoto obligations and to cut dependence on oil, Japan has started importing biofuels from Brazil and elsewhere. And even though the country has limited local bioenergy potential, its Agriculture Ministry will begin a search for natural resources, including farm products and their residues, that can be used to make biofuels in Japan. To this end, studies will be conducted at 900 locations nationwide over a three-year period.
The Japan Times - Jan. 12, 2007.
 Chrysler's chief economist Van Jolissaint has launched an arrogant attack on "quasi-hysterical Europeans" and their attitudes to global warming, calling the Stern Review 'dubious'. The remarks illustrate the yawning gap between opinions on climate change among Europeans and Americans, but they also strengthen the view that announcements by US car makers and legislators about the development of green vehicles are nothing more than window dressing. Today, the EU announced its comprehensive energy policy for the 21st century, with climate change at the center of it.
BBC News - Jan. 10, 2007. Chrysler's chief economist Van Jolissaint has launched an arrogant attack on "quasi-hysterical Europeans" and their attitudes to global warming, calling the Stern Review 'dubious'. The remarks illustrate the yawning gap between opinions on climate change among Europeans and Americans, but they also strengthen the view that announcements by US car makers and legislators about the development of green vehicles are nothing more than window dressing. Today, the EU announced its comprehensive energy policy for the 21st century, with climate change at the center of it.
BBC News - Jan. 10, 2007.
 The new Canadian government is investing $840,000 into BioMatera Inc. a biotech company that develops industrial biopolymers (such as PHA) that have wide-scale applications in the plastics, farmaceutical and cosmetics industries. Plant-based biopolymers such as PHA are biodegradable and renewable.
Government of Canada - Jan. 9, 2007. The new Canadian government is investing $840,000 into BioMatera Inc. a biotech company that develops industrial biopolymers (such as PHA) that have wide-scale applications in the plastics, farmaceutical and cosmetics industries. Plant-based biopolymers such as PHA are biodegradable and renewable.
Government of Canada - Jan. 9, 2007.

|
|
|
|
|
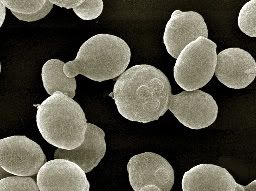 Earlier this week, researchers identified which genes a bacterium activates to select the enzymes for the breakdown of cellulose into sugars. The discovery is important for the future of cellulosic ethanol production (earlier post). Another group of scientists discovered similar cellulase genes in the guts of termites - creatures famed for their capacity to break down wood efficiently (earlier post).
Earlier this week, researchers identified which genes a bacterium activates to select the enzymes for the breakdown of cellulose into sugars. The discovery is important for the future of cellulosic ethanol production (earlier post). Another group of scientists discovered similar cellulase genes in the guts of termites - creatures famed for their capacity to break down wood efficiently (earlier post). biomass :: bioenergy :: biofuels :: energy :: sustainability :: cellulose :: lignin :: xylose :: wood :: biomass :: genomics :: biotechnology ::
biomass :: bioenergy :: biofuels :: energy :: sustainability :: cellulose :: lignin :: xylose :: wood :: biomass :: genomics :: biotechnology ::  --------------
--------------


 Saab will introduce its BioPower flex-fuel options to its entire 9-3 range, including Sport Sedan, SportCombi and Convertible bodystyles, at the Geneva auto show.
Saab will introduce its BioPower flex-fuel options to its entire 9-3 range, including Sport Sedan, SportCombi and Convertible bodystyles, at the Geneva auto show.








0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Links to this post:
Create a Link
<< Home